NAME
sccs-get, get − retrieve a version of an SCCS file
SYNOPSIS
/usr/ccs/bin/get [-begkmnpst] [ -l [p]] [-asequence] [-c date-time | -cdate-time] [-Gg-file] [-i sid-list | -isid-list] [ -r [sid]] [-x sid-list | -xsid-list] s.filename...
/usr/xpg4/bin/get [-begkmnpst] [ -l [p]] [-asequence] [-c date-time | -cdate-time] [-Gg-file] [-i sid-list | -isid-list] [-r sid | -rsid] [-x sid-list | -xsid-list] s.filename...
DESCRIPTION
The get utility retrieves a working copy from the SCCS history file, according to the specified options.
For each s.filename argument, get displays the SCCS delta ID (SID) and number of lines retrieved.
If a directory name is used in place of the s.filename argument, the get command applies to all s.files in that directory. Unreadable s.files produce an error; processing continues with the next file (if any). The use of ’−’ as the s.filename argument indicates that the names of files are to be read from the standard input, one s.file per line.
The retrieved file normally has the same filename base as the s.file, less the prefix, and is referred to as the g-file.
For each file processed, get responds (on the standard output) with the SID being accessed, and with the number of lines retrieved from the s.file.
OPTIONS
The following options are supported:
|
-b |
Create a new branch. Used with the -e option to indicate that the new delta should have an SID in a new branch. Instead of incrementing the level for version to be checked in, get indicates in the p.file that the delta to be checked in should either initialize a new branch and sequence (if there is no existing branch at the current level), or increment the branch component of the SID. If the b flag is not set in the s.file, this option is ignored. | ||
|
-e |
Retrieve a version for editing. With this option, get places a lock on the s.file, so that no one else can check in changes to the version you have checked out. If the j flag is set in the s.file, the lock is advisory: get issues a warning message. Concurrent use of ’get -e’ for different SIDs is allowed;however, get will not check out a version of the file if a writable version is present in the directory. All SCCS file protections stored in the s.file, including the release ceiling, floor, and authorized user list, are honored by ’get -e’. | ||
|
-g |
Get the SCCS version ID, without retrieving the version itself. Used to verify the existence of a particular SID. | ||
|
-k |
Suppress expansion of ID keywords. -k is implied by the -e. | ||
|
-m |
Precede each retrieved line with the SID of the delta in which it was added to the file. The SID is separated from the line with a TAB. | ||
|
-n |
Precede each line with the %M% ID keyword and a TAB. When both the -m and -n options are used, the ID keyword precedes the SID, and the line of text. | ||
|
-p |
Write the text of the retrieved version to the standard output. All messages that normally go to the standard output are written to the standard error instead. | ||
|
-s |
Suppress all output normally written on the standard output. However, fatal error messages (which always go to the standard error) remain unaffected. | ||
|
-t |
Retrieve the most recently created (top) delta in a given release (for example: -r1). | ||
|
-l[p] |
Retrieve a summary of the delta table (version log) and write it to a listing file, with the ’l.’ prefix (called ’l.file’). When -lp is used, write the summary onto the standard output. |
-asequence
Retrieve the version corresponding to the indicated delta sequence number. This option is used primarily by the SCCS comb command (see sccs-comb(1)); for users, -r is an easier way to specify a version. -a supersedes -r when both are used.
-c date-time | -cdate-time
Retrieve the latest version checked in prior to the date and time indicated by the date-time argument. date-time takes the form:
yy[mm[dd[ hh[mm[ss]]]]]
Units omitted from the indicated date and time default to their maximum possible values; that is -c7502 is equivalent to -c750228235959. Values of yy in the range 69−99 refer to the twentieth century. Values in the range 00−68 refer to the twenty-first century. Any number of non-numeric characters may separate the various 2 digit components. If white-space characters occur, the date-time specification must be quoted.
-Gnewname
Use newname as the name of the retrieved version.
-i sid-list | -isid-list
Specify a list of deltas to include in the retrieved version. The included deltas are noted in the standard output message. sid-list is a comma-separated list of SIDs. To specify a range of deltas, use a ’−’ separator instead of a comma, between two SIDs in the list.
/usr/ccs/bin/get
-r[sid]
Retrieve the version corresponding to the indicated SID (delta).
The SID for a given delta is a number, in Dewey decimal format, composed of two or four fields: the release and level fields, and for branch deltas, the branch and sequence fields. For instance, if 1.2 is the SID, 1 is the release, and 2 is the level number. If 1.2.3.4 is the SID, 3 is the branch and 4 is the sequence number.
You need not specify the entire SID to retrieve a version with get. When you omit -r altogether, or when you omit both release and level, get normally retrieves the highest release and level. If the d flag is set to an SID in the s.file and you omit the SID, get retrieves the default version indicated by that flag.
When you specify a release but omit the level, get retrieves the highest level in that release. If that release does not exist, get retrieves highest level from the next-highest existing release.
Similarly with branches, if you specify a release, level and branch, get retrieves the highest sequence in that branch.
/usr/xpg4/bin/get
-r sid | -rsid
Same as for /usr/ccs/bin/get except that SID is mandatory.
-x sid-list | -xsid-list
Exclude the indicated deltas
from the retrieved version. The excluded deltas are noted in
the standard output message. sid-list is a
comma-separated list of SIDs. To specify a range of
deltas, use a
’−’ separator instead of a comma,
between two SIDs in the list.
OUTPUT
/usr/ccs/bin/get
The output format for /usr/ccs/bin/get is as
follows:
"%s\n%d lines\n", <SID>, <number of lines>
/usr/xpg4/bin/get
The output format for /usr/xpg4/bin/get is as
follows:
"%s\n%d\n", <SID>, <number of lines>
USAGE
ID
Keywords
In the absence of -e or -k, get expands
the following ID keywords by replacing them with the
indicated values in the text of the retrieved source.
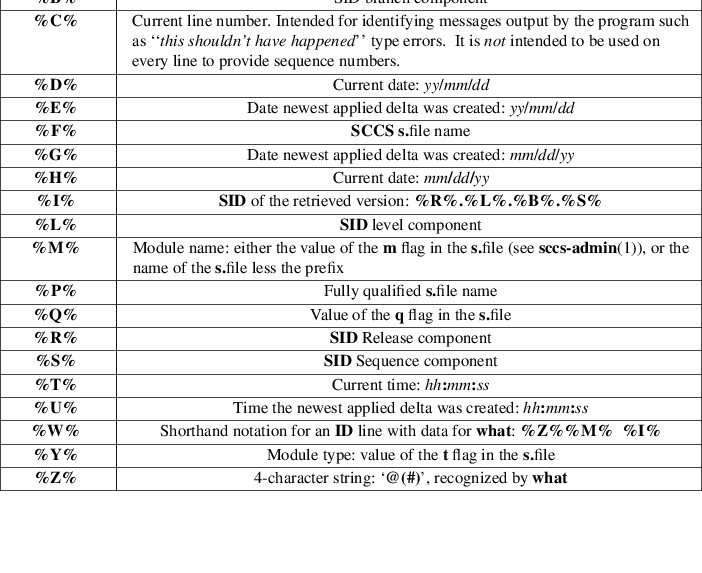
ID String
The table below explains how the SCCS identification
string is determined for retrieving and creating deltas.

|
(1) |
’R’, ’L’, ’B’, and ’S’ are the ’release’, ’level’, ’branch’, and ’sequence’ components of the SID, respectively; ’m’ means ’maximum’. Thus, for example, ’R.mL’ means ’the maximum level number within release R’; ’R.L.(mB+1).1’ means ’the first sequence number on the new branch (that is, maximum branch number plus one) of level L within release R’. Note: if the SID specified is of the form ’R.L’, ’R.L.B’, or ’R.L.B.S’, each of the specified components must exist. | ||
|
(2) |
The -b option is effective only if the b flag is present in the file. An entry of ’−’ means ’irrelevant’. | ||
|
(3) |
This case applies if the d (default SID) flag is not present in the file. If the d flag is present in the file, the SID obtained from the d flag is interpreted as if it had been specified on the command line. Thus, one of the other cases in this table applies. | ||
|
(4) |
Forces creation of the first delta in a new release. | ||
|
(5) |
’hR’ is the highest existing release that is lower than the specified, nonexistent, release R. | ||
|
(6) |
Successor. |
FILES
’’g-file’’
version retrieved by get
l.file
file containing extracted delta table info
p.file
permissions (lock) file
z.file
temporary copy of s.file
ATTRIBUTES
See attributes(5) for descriptions of the following attributes:
/usr/ccs/bin/get

/usr/xpg4/bin/get

SEE ALSO
sccs(1), sccs-admin(1), sccs-delta(1), sccs-help(1), sccs-prs(1), sccs-prt(1), sccs-sact(1), sccs-unget(1), what(1), sccsfile(4), attributes(5), XPG4(5)
DIAGNOSTICS
Use the SCCS help command for explanations (see sccs-help(1)).
BUGS
If the effective user has write permission (either explicitly or implicitly) in the directory containing the SCCS files, but the real user does not, only one file may be named when using -e.