NAME
conky - A system monitor for X
SYNOPSIS
conky [ options ]
DESCRIPTION
Conky is a system monitor for X originally based on torsmo. Since its inception, Conky has changed significantly from its predecessor, while maintaining simplicity and configurability. Conky can display just about anything, either on your root desktop or in its own window. Not only does Conky have many built-in objects, it can also display just about any piece of information by using scripts and other external programs.
Conky has more than 250 built in objects, including support for a plethora of OS stats (uname, uptime, CPU usage, mem usage, disk usage, "top" like process stats, and network monitoring, just to name a few), built in IMAP and POP3 support, built in support for many popular music players (MPD, XMMS2, Audacious), and much much more. Conky can display this info either as text, or using simple progress bars and graph widgets, with different fonts and colours.
We are always looking for help, whether its reporting bugs, writing patches, or writing docs. Please use the facilities on GitHub to make bug reports, feature requests, and submit patches.
Thanks for your interest in Conky.
COMPILING
For users compiling from source on a binary distro, make sure you have the X development libraries installed (Unless you configure your build without X11). This should be a package along the lines of "libx11-dev" or "xorg-x11-dev" for X11 libs, and similar "-dev" format for the other libs required (depending on your build options). You should be able to see which extra packages you need to install by reading errors that you get from running `cmake'. The easiest way to view the available build options is to run `ccmake' or `cmake-gui' from the source tree, but be careful when disabling certain features as you may lose desired functionality. E.g., with BUILD_MATH disabled you won't get errors but logarithmic graphs will be normal graphs and gauges will miss their line.
Conky has (for some time) been available in the repositories of most popular distributions. Here are some installation instructions for a few:
Gentoo users -- Conky is in Gentoo's Portage... simply use "emerge app-admin/conky" for installation.
Debian, etc. users -- Conky should be in your repositories, and can be installed by doing "aptitude install conky".
Example to
compile and run Conky with default components (note that
some build options may differ for your system):
cmake -D CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX:string=/usr .
|
make |
make install # Optional
src/conky
Conky has been tested to be compatible with C99 C and C++0x C++, however it has not been tested with anything other than gcc, and is not guaranteed to work with other compilers.
TIP: Try configuring Conky with `ccmake' or `cmake-gui' instead of just `cmake'.
YOU SHOULD KNOW
Conky is generally very good on resources. That said, the more you try to make Conky do, the more resources it is going to consume.
An easy way to force Conky to reload your ~/.config/conky/conky.conf: "killall -SIGUSR1 conky". Saves you the trouble of having to kill and then restart.
OPTIONS
Command line
options override configurations defined in configuration
file.
-a | --alignment= ALIGNMENT
Text alignment on screen, {top,bottom,middle}_{left,right,middle} or none. Can also be abbreviated with first chars of position, ie. tr for top_right. Only available with build flag BUILD_X11 enabled.
-b | --double-buffer
Use double buffering (eliminates "flicker"). Only available with build flag BUILD_X11 enabled.
-c | --config= FILE
Config file to load instead of ~/.config/conky/conky.conf.
-C | --print-config
Print builtin default config to stdout. See also the section EXAMPLES for more information. Only available with build flag BUILD_BUILTIN_CONFIG enabled.
-d | --daemonize
Daemonize Conky, aka fork to background.
-D | --debug
Increase debugging output, ie. -DD for more debugging.
-f | --font= FONT
Font to use. Only available with build flag BUILD_X11 enabled.
-h | --help
Prints command line help and exits.
-i COUNT
Number of times to update Conky (and quit).
-o | --own-window
Create own window to draw. Only available with build flag BUILD_X11 enabled.
-p | --pause= SECONDS
Time to pause/wait before actually starting Conky.
-q | --quiet
Run Conky in 'quiet mode' (ie. no output).
-t | --text= TEXT
Text to render, remember single quotes, like -t ' $uptime '.
-u | --interval= SECONDS
Update interval.
-v | -V | --version
Prints version, build information and general info. Exits after printing.
-w | --window-id= WIN_ID
Window id to draw. Only available with build flag BUILD_X11 enabled.
-x X_COORDINATE
X position.
-X | --display= DISPLAY
X11 display to use. Only available with build flag BUILD_X11 enabled.
-y Y_COORDINATE
Y position.
CONFIGURATION SETTINGS
This is a listing of global configuration options for Conky. These are placed in the conky.config section of your configuration file, before conky.text.
The default configuration file location is ~/.config/conky/conky.conf or ${sysconfdir}/conky/conky.conf. On most systems, $sysconfdir is /etc, and you can find the sample config file there in /etc/conky/conky.conf.
You might want to copy the default config to ~/.config/conky/conky.conf and then start modifying it. User configs can be found at https://github.com/brndnmtthws/conky/wiki/Configs.
Optional
arguments are generally denoted with paretheses (i.e.,
(optional)).
alignment
Aligned position on screen, may be none or one of:

In case of panel and dock windows, it might make more sense to use one of the following aliases:

See also gap_x and gap_y settings.
append_file
Append the file given as argument.
background
Boolean value, if true, Conky will be forked to background when started.
border_inner_margin
Inner border margin in pixels (the margin between the border and text).
border_outer_margin
Outer border margin in pixels (the margin between the border and the edge of the window).
border_width
Border width in pixels.
|
colorN |
Predefine a color for use inside conky.text segments. Substitute N by a digit between 0 and 9, inclusively. When specifying the color value in hex, omit the leading hash (#). |
console_bar_fill
A character to fill the console bars.
Default: #
console_bar_unfill
A character to unfill the console bars.
Default: .
console_graph_ticks
A comma-separated list of strings to use as the bars of a graph output to console/shell. The first list item is used for the minimum bar height and the last item is used for the maximum, e.g. " ,_,=,#".
cpu_avg_samples
The number of samples to average for CPU monitoring.
default_bar_height
Specify a default height for bars.
Default: 6
default_bar_width
Specify a default width for bars. If not specified, the default value is 0, which causes the bar to expand to fit the width of your Conky window. If you set out_to_console = true, the default value will be 10 for the text version of the bar.
default_color
Default color and border color.
default_gauge_height
Specify a default height for gauges.
Default: 25
default_gauge_width
Specify a default width for gauges.
Default: 40
default_graph_height
Specify a default height for graphs.
Default: 25
default_graph_width
Specify a default width for graphs. If not specified, the default value is 0, which causes the graph to expand to fit the width of your Conky window. If you set out_to_console = true, the text version of the graph will actually have no width and you will need to set a sensible default or set the height and width of each graph individually.
default_outline_color
Default outline color.
default_shade_color
Default shading color and border’s shading color.
detect_battery
One or more batteries to check in order to use update_interval_on_battery (comma separated).
Default: BAT0
disable_auto_reload
Enable to disable the inotify-based auto config reload feature.
diskio_avg_samples
The number of samples to average for disk I/O monitoring.
display
Specify an X display to connect to.
double_buffer
Use the Xdbe extension? (eliminates flicker) It is highly recommended to use own window with this one so double buffer won’t be so big.
draw_blended
Boolean, blend when rendering drawn image? Some images blend incorrectly breaking alpha with ARBG visuals. This provides a possible work around by disabling blending.
Default: True
draw_borders
Draw borders around text.
draw_graph_borders
Draw borders around graphs.
draw_outline
Draw outlines.
draw_shades
Draw shades.
extra_newline
Put an extra newline at the end when writing to stdout, useful for writing to awesome’s wiboxes.
|
font |
Font name in X, xfontsel can be used to get a nice font. | ||
|
fontN |
Predefine a font to be used in conky.text segments. Substitute N by a number between 0 and 9 inclusive. Use the same format as a font variable. |
forced_redraw
Boolean value, if true, Conky will redraw everything when you switch the workspace. This may cause delays/flickering on some WMs.
format_human_readable
If enabled, values which are in bytes will be printed in human readable format (i.e., KiB, MiB, etc). If disabled, the number of bytes is printed instead.
|
gap_x |
Gap, in pixels, between right or left border of screen, same as passing -x at command line, e.g. gap_x 10. For other position related stuff, see ’alignment’. | ||
|
gap_y |
Gap, in pixels, between top or bottom border of screen, same as passing -y at command line, e.g. gap_y 10. For other position related stuff, see ’alignment’. |
github_token
Specify API token for GitHub notifications.
Create an API token at https://github.com/settings/tokens/new?scopes=notifications&description=conky.
graph_gradient_mode (rgb|hcl|hsv)
Changes the color space used for interpolation. Arguments are hcl, hsv, and rgb (default).
Default: rgb
hddtemp_host
Hostname to connect to for hddtemp objects.
Default: 127.0.0.1
hddtemp_port
Port to use for hddtemp connections.
Default: 7634
http_port
Port to listen to for HTTP connections. Default value is 10080, but is blocked by Firefox and Chrome, so you really want to change it.
Default: 10080
http_refresh
When this is set the page generated with out_to_http will automatically refresh each interval.
if_up_strictness
How strict should if_up be when testing an interface for being up? The value is one of up, link or address, to check for the interface being solely up, being up and having link or being up, having link and an assigned IP address.
imap host user pass
[’-i interval (in seconds)’] [“-f
’folder’”] [’-p
port’] [“-e ’command’”]
[’-r retries’]
Default global IMAP server. Default port is 143, default folder is ’INBOX’, default interval is 5 minutes, and default number of retries before giving up is 5. If the password is supplied as ’*’, you will be prompted to enter the password when Conky starts.
imlib_cache_flush_interval
Interval (in seconds) to flush Imlib2 cache.
imlib_cache_size
Imlib2 image cache size, in bytes. Increase this value if you use $image lots. Set to 0 to disable the image cache.
Default: 4194304
lowercase
Boolean value, if true, text is rendered in lower case.
lua_draw_hook_post function_name [’function arguments’]
This function, if defined, will be called by Conky through each iteration after drawing to the window. Requires X support. Takes any number of optional arguments. Use this hook for drawing things on top of what Conky draws. Conky puts ’conky_’ in front of function_name to prevent accidental calls to the wrong function unless you place ’conky_’ in front of it yourself.
lua_draw_hook_pre function_name [’function arguments’]
This function, if defined, will be called by Conky through each iteration before drawing to the window. Requires X support. Takes any number of optional arguments. Use this hook for drawing things on top of what Conky draws. Conky puts ’conky_’ in front of function_name to prevent accidental calls to the wrong function unless you place ’conky_’ in front of it yourself.
lua_load
Loads the Lua scripts separated by spaces.
lua_mouse_hook function_name
This function, if defined, will be called by Conky upon receiving mouse events from X or Wayland. A table containing event information will be passed to this function as the first argument. Use this hook for detecting mouse input and acting on it. Conky requires that the function declaration has a ’conky_’ prefix to prevent accidental calls to the wrong function.
lua_shutdown_hook function_name [’function arguments’]
This function, if defined, will be called by Conky at shutdown or when the configuration is reloaded. Use this hook to clean up after yourself, such as freeing memory which has been allocated by external libraries via Lua. Conky puts ’conky_’ in front of function_name to prevent accidental calls to the wrong function unless you place ’conky_’ in front of it yourself.
lua_startup_hook function_name [’function arguments’]
This function, if defined, will be called by Conky at startup or when the configuration is reloaded. Use this hook to initialize values, or for any run-once applications. Conky puts ’conky_’ in front of function_name to prevent accidental calls to the wrong function unless you place ’conky_’ in front of it yourself.
mail_spool
Mail spool for mail checking.
max_port_monitor_connections
Allow each port monitor to track at most this many connections.
Default: 256
max_text_width integer_number
When a line in the output contains ’width’ chars and the end isn’t reached, the next char will start on a new line. If you want to make sure that lines don’t get broken, set ’width’ to 0.
max_user_text integer_number
Maximum size of user text buffer in bytes, i.e. text inside conky.text section in config file.
Default: 16384
maximum_width integer_number
Maximum width of window.
minimum_height integer_number
Minimum height of the window.
minimum_width integer_number
Minimum width of window.
mpd_host
Host of MPD server.
mpd_password
MPD server password.
mpd_port
Port of MPD server.
music_player_interval
Music player thread update interval.
Default: update interval
mysql_db
MySQL database to use.
Default: mysql
mysql_host
Host of MySQL server
Default: localhost
mysql_password
Password of the MySQL user. Place it between "-chars. When this is not set there is no password used.
mysql_port
Port of MySQL server.
mysql_user
MySQL user name to use when connecting to the server. Defaults to your username.
net_avg_samples
The number of samples to average for net data.
no_buffers
Subtract (file system) buffers from used memory.
nvidia_display
The display that the nvidia variable will used.
Default: $DISPLAY
out_to_console
Print text to stdout.
out_to_http
Let conky act as a small http-server serving its text.
out_to_ncurses
Print text in the console, but use ncurses so that conky can print the text of a new update over the old text. (In the future this will provide more useful things).
out_to_stderr
Print text to stderr.
out_to_wayland
Open a Wayland window to display output.
out_to_x
When set to no, there will be no output in X (useful when you also use things like out_to_console). If you set it to no, make sure that it’s placed before all other X-related setting (take the first line of your configfile to be sure).
Default: True
override_utf8_locale
Force UTF8. Requires XFT.
overwrite_file
Overwrite the file given as argument.
own_window
Boolean, draw conky in own window instead of drawing on root window.
own_window_argb_value integer_number
When ARGB visuals are enabled, this use this to modify the alpha value used. Valid range is 0-255, where 0 is 0% opacity, and 255 is 100% opacity.
Default: 255
own_window_argb_visual
Boolean, use ARGB visual? ARGB can be used for real transparency, note that a composite manager is required on X11. This option will not work as desired (in most cases) in conjunction with ’own_window_type override’.
own_window_class
Manually set the WM_CLASS name.
Default: Conky
own_window_colour color
If own_window_transparent no, set a specified background colour. Takes either a hex value (e.g. ’#ffffff’), a shorthand hex value (e.g. ’#fff’), or a valid RGB name (see /usr/lib/X11/rgb.txt).
Default: black
own_window_hints hint(,hint)*
If own_window is set, on X11 you may specify comma separated window manager hints to affect the way Conky displays.
Following hints are some of the standard WM specification ones: - above indicates that conky should be on top of most windows. - below indicates that conky should be below most windows. - skip_pager indicates that conky should not be included on a Pager. Implied if own_window_type is ’dock’ or ’panel’. - skip_taskbar indicates that conky should not be included on a taskbar. Implied if own_window_type is ’dock’ or ’panel’. - sticky indicates that the Window Manager SHOULD keep conky’s position fixed on the screen, even when the virtual desktop scrolls. - undecorated indicates that conky shouldn’t have any window decorations (e.g. title bar). Implied if own_window_type is ’dock’ or ’panel’.
Notes: - Use own_window_type='desktop' setting as another way to implement many of these hints implicitly. - If you use own_window_type='override', window manager hints have no meaning and are ignored.
own_window_title
Allows overriding conky window name.
Default: conky ()
own_window_transparent
Make conky window transparent. If own_window_argb_visual is enabled, sets background opacity to 0%.
own_window_type (normal|desktop|dock|panel|utility|override)
If own_window is set, under X11 you can specify type of window conky displayed as:
|
• |
normal mode makes conky show as normal window. This mode can be configured with use of own_window_hints setting. | ||
|
• |
desktop windows are special windows that have no window decorations, are always visible on the desktop, do not appear in pager or taskbar, and are sticky across all workspaces. Many DEs include desktop windows for background, icons and desktop menu, in those cases it might be better to use normal or one of the below options, as those will cover conky when they’re clicked on. | ||
|
• |
dock windows reserve space on the desktop, i.e. WMs will try their best to not place windows on top of them. They’re the same as desktop in other respects, but render on top of desktop windows. | ||
|
• |
panel windows are similar to dock windows, but they also reserve space along a desktop edge (like taskbars), preventing maximized windows from overlapping them. The edge is chosen based on the alignment setting. | ||
|
• |
utility windows are persistent utility windows (e.g. a palette or toolbox). They appear on top of other windows (in the same group), but otherwise behave much like normal windows. | ||
|
• |
override windows are drawn directly on root window (desktop background) and are not under the control of the window manager. These will not work with DEs which draw desktop icons via custom panels/windows as those will cover conky. own_window_hints are ignored for override windows. |
To make conky mount on root window, set own_window to false.
Default: normal
pad_percents
Pad percentages to this many decimals (0 = no padding).
pop3 host user pass
[’-i interval (in seconds)’] [’-p
port’] [“-e
’command’”] [’-r
retries’]
Default global POP3 server. Arguments are: `host user pass [-i interval (in seconds)] [-p port] [-e ’command’] [-r retries]". Default port is 110, default interval is 5 minutes, and default number of retries before giving up is 5. If the password is supplied as ’*’, you will be prompted to enter the password when Conky starts.
short_units
Shortens units to a single character (kiB->k, GiB->G, etc.).
show_graph_range
Shows the time range covered by a graph.
show_graph_scale
Shows the maximum value in scaled graphs.
stippled_borders
Border stippling (dashing) in pixels.
store_graph_data_explicitly
Enable storing graph data explicitly by ID. This avoids resets while using conditional colors. This option should be disabled while using graphs indirectly e.g. via execpi or lua_parse. Otherwise the graph stays emtpy. The default value is true.
Default: True
temperature_unit
Desired output unit of all objects displaying a temperature. Parameters are either fahrenheit or celsius.
Default: celsius
templateN
Define a template for later use inside conky.text segments. Substitute N by a digit between 0 and 9, inclusively. The value of the variable is being inserted into the stuff inside conky.text at the corresponding position, but before some substitutions are applied:
|
• |
\\n -> newline |
|||
|
• |
\\ -> backslash |
|||
|
• |
\\ -> space |
|||
|
• |
\\N -> template argument N (starting from 1) |
text_buffer_size seconds
Size of the standard text buffer (default is 256 bytes). This buffer is used for intermediary text, such as individual lines, output from $exec vars, and various other variables. Increasing the size of this buffer can drastically reduce Conky’s performance, but will allow for more text display per variable. The size of this buffer cannot be smaller than the default value of 256 bytes.
times_in_seconds
If true, variables that output times output a number that represents seconds. This doesn’t affect $time, $tztime and $utime.
top_cpu_separate
If true, cpu in top will show usage of one processor’s power. If false, cpu in top will show the usage of all processors’ power combined.
top_name_verbose
If true, top name shows the full command line of each process, including arguments (whenever possible). Otherwise, only the basename is displayed. Default value is false.
top_name_width
Width for $top name value (defaults to 15 characters).
total_run_times
Total number of times for Conky to update before quitting. Zero makes Conky run forever.
units_spacer
String to place between values and units.
update_interval seconds
Update interval.
update_interval_on_battery seconds
Update interval when running on battery power.
uppercase
Boolean value, if true, text is rendered in upper case.
use_spacer
Adds spaces around certain objects to stop them from moving other things around. Arguments are left, right, and none (default). The old true/false values are deprecated and default to right/none respectively. Note that this only helps if you are using a mono font, such as Bitstream Vera Sans Mono.
Default: none
use_xft
Use Xft (anti-aliased font and stuff).
xftalpha
Alpha of Xft font. Must be a value at or between 1 and 0.
xinerama_head
Specify a Xinerama head.
OBJECTS/VARIABLES
To configure what Conky displays, you must supply some variables in the conky.text section of your configuration. In this secton you’ll find a listing of the available variables. Some of them may require build options to be enabled at compile time for them to work.
Colours are parsed using XParseColor(), there might be a list of them: /usr/share/X11/rgb.txt. Colour can be also in #rrggbb format (hex).
Some objects may create threads, and sometimes these threads will not be destroyed until Conky terminates. There is no way to destroy or clean up threads while Conky is running. For example, if you use an MPD variable, the MPD thread will keep running until Conky dies. Some threaded objects will use one of the parameters as a key, so that you only have 1 relevant thread running (for example, the $curl, and $rss objects launch one thread per URI).
Optional
arguments are generally denoted with paretheses (i.e.,
(optional)).
acpiacadapter (adapter)
ACPI AC adapter state. On linux, the adapter option specifies the subfolder of /sys/class/power_supply containing the state information (tries AC and ADP1 if there is no argument given). Non-linux systems ignore it.
acpifan
ACPI fan state.
acpitemp
ACPI temperature in C.
addr (interface)
IP address for an interface, or “No Address” if no address is assigned.
addrs (interface)
IP addresses for an interface (if one - works like addr). Linux only.
adt746xcpu
CPU temperature from therm_adt746x.
adt746xfan
Fan speed from therm_adt746x.
alignc (num)
Align text to centre.
alignr (num)
Right-justify text, with space of N.
apcupsd host port
Sets up the connection to apcupsd daemon. Prints nothing.
Default: localhost:3551
apcupsd_cable
Prints the UPS connection type.
apcupsd_charge
Current battery capacity in percent.
apcupsd_lastxfer
Reason for last transfer from line to battery.
apcupsd_linev
Nominal input voltage.
apcupsd_load
Current load in percent.
apcupsd_loadbar
Bar showing current load.
apcupsd_loadgauge (height),(width)
Gauge that shows current load.
apcupsd_loadgraph
(height),(width) (gradient colour 1) (gradient colour
2) (scale) (-t) (-l)
History graph of current load.
apcupsd_model
Prints the model of the UPS.
apcupsd_name
Prints the UPS user-defined name.
apcupsd_status
Prints current status (on-line, on-battery).
apcupsd_temp
Current internal temperature.
apcupsd_timeleft
Time left to run on battery.
apcupsd_upsmode
Prints the UPS mode (e.g. standalone).
apm_adapter
Display APM AC adapter status. FreeBSD, OpenBSD only.
apm_battery_life
Display APM battery life in percent. FreeBSD, OpenBSD only.
apm_battery_time
Display remaining APM battery life in hh:mm:ss or “unknown” if AC adapterstatus is on-line or charging. FreeBSD, OpenBSD only.
audacious_bar (height),(width)
Progress bar.
audacious_bitrate
Bitrate of current tune.
audacious_channels
Number of audio channels of current tune.
audacious_filename
Full path and filename of current tune.
audacious_frequency
Sampling frequency of current tune.
audacious_length
Total length of current tune as MM:SS.
audacious_length_seconds
Total length of current tune in seconds.
audacious_main_volume
The current volume fetched from Audacious.
audacious_playlist_length
Number of tunes in playlist.
audacious_playlist_position
Playlist position of current tune.
audacious_position
Position of current tune (MM:SS).
audacious_position_seconds
Position of current tune in seconds.
audacious_status
Player status (Playing/Paused/Stopped/Not running).
audacious_title (max length)
Title of current tune with optional maximum length specifier.
battery (num)
Battery status and remaining percentage capacity of ACPI or APM battery. ACPI battery number can be given as argument.
Default: BAT0
battery_bar (height),(width) (num)
Battery percentage remaining of ACPI battery in a bar. ACPI battery number can be given as argument (use all to get the mean percentage remaining for all batteries).
Default: BAT0
battery_percent (num)
Battery percentage remaining for ACPI battery. ACPI battery number can be given as argument (use all to get the mean percentage remaining for all batteries).
Default: BAT0
battery_power_draw (num)
Battery power draw in watts
Default: BAT0
battery_short (num)
Battery status and remaining percentage capacity of ACPI or APM battery. ACPI battery number can be given as argument. This mode display a short status, which means that C is displayed instead of charging, D for discharging, F for full, N for not present, E for empty and U for unknown.
Default: BAT0
battery_status (num)
Battery status for ACPI battery. ACPI battery number can be given as arguments.
Default: BAT0
battery_time (num)
Battery charge/discharge time remaining of ACPI battery. ACPI battery number can be given as argument.
Default: BAT0
blink text_and_other_conky_vars
Let ’text_and_other_conky_vars’ blink on and off.
buffers
Amount of memory buffered.
|
cached |
Amount of memory cached. |
cat file
Reads a file and displays the contents in conky. This is useful if you have an independent process generating output that you want to include in conky.
catp file
Reads a file and displays the contents in conky. This is useful if you have an independent process generating output that you want to include in conky. This differs from $cat in that it parses the contents of the file, so you can insert things like `${color red}hi!${color}` in your file and have it correctly parsed by Conky.
cmdline_to_pid string
PID of the first process that has string in its commandline.
cmus_aaa
Print aaa status of cmus (all/artist/album).
cmus_album
Prints the album of the current cmus song.
cmus_artist
Prints the artist of the current cmus song.
cmus_curtime
Current time of the current cmus song.
cmus_date
Print the date of the current cmus song.
cmus_file
Print the file name of the current cmus song.
cmus_genre
Print the genre name of the current cmus song.
cmus_percent
Percent of song’s progress.
cmus_progress (height),(width)
cmus’ progress bar.
cmus_random
Random status of cmus (on/off).
cmus_repeat
Repeat status of cmus (song/all/off).
cmus_state
Current state of cmus (playing, paused, stopped etc).
cmus_timeleft
Time left of the current cmus song.
cmus_title
Prints the title of the current cmus song.
cmus_totaltime
Total length of the current cmus song.
cmus_track
Print track number of current cmus song.
color (color)
Change drawing color to color which is a name of a color or a hexcode preceded with #, e.g. #0A1B2C. If you use ncurses only the following colors are supported: red, green, yellow, blue, magenta, cyan, black, and white.
|
colorN |
Change drawing color to colorN configuration option, where N is a digit between 0 and 9, inclusively. |
combine var1 var2
Places the lines of var2 to the right of the lines of var1 separated by the chars that are put between var1 and var2. For example: ${combine ${head /proc/cpuinfo 2} - ${head /proc/meminfo 1}} gives as output cpuinfo_line1 - meminfo_line1 on line 1 and cpuinfo_line2 - on line 2. $combine vars can also be nested to place more vars next to each other.
conky_build_arch
CPU architecture Conky was built for.
conky_version
Conky version.
cpu (cpuN)
CPU usage in percents. For SMP machines, the CPU number can be provided as an argument. ${cpu cpu0} is the total usage, and ${cpu cpuX} (X >= 1) are individual CPUs.
cpubar (cpuN) (height),(width)
Bar that shows CPU usage, height is bar’s height in pixels. See $cpu for more info on SMP.
cpugauge (cpuN) (height),(width)
Elliptical gauge that shows CPU usage, height and width are gauge’s vertical and horizontal axis respectively. See $cpu for more info on SMP.
cpugovernor (cpuN)
The active CPU scaling governor, defaulting to the first core. See $cpu for more info on SMP. Linux only.
cpugraph (cpuN)
(height),(width) (gradient colour 1) (gradient colour
2) (scale) (-t) (-l)
CPU usage graph, with optional colours in hex, minus the #. See $cpu for more info on SMP. Uses a logarithmic scale (to see small numbers) when you use the -l switch. Takes the switch ’-t’ to use a temperature gradient, which makes the gradient values change depending on the amplitude of a particular graph value (try it and see).
curl url (interval_in_minutes)
Download data from URI using Curl at the specified interval. The interval may be a positive floating point value (0 is allowed), otherwise defaults to 15 minutes. Most useful when used in conjunction with Lua and the Lua API. This object is threaded, and once a thread is created it can’t be explicitly destroyed. One thread will run for each URI specified. You can use any protocol that Curl supports.
desktop
Number of the desktop on which conky is running or the message “Not running in X” if this is the case.
desktop_name
Name of the desktop on which conky is running or the message “Not running in X” if this is the case.
desktop_number
Number of desktops or the message “Not running in X” if this is the case.
disk_protect device
Disk protection status, if supported (needs kernel-patch). Prints either “frozen” or “free” (note the padding).
diskio (device)
Displays current disk IO. Device is optional, and takes the form of sda for /dev/sda. A block device label can be specified with label:foo and a block device partuuid can be specified with partuuid:40000000-01.
diskio_read (device)
Displays current disk IO for reads. Device as in diskio.
diskio_write (device)
Displays current disk IO for writes. Device as in diskio.
diskiograph (device)
(height),(width) (gradient colour 1) (gradient
colour 2) (scale) (-t) (-l)
Disk IO graph, colours defined in hex, minus the #. If scale is non-zero, it becomes the scale for the graph. Uses a logarithmic scale (to see small numbers) when you use -l switch. Takes the switch ’-t’ to use a temperature gradient, which makes the gradient values change depending on the amplitude of a particular graph value (try it and see).
diskiograph_read (device)
(height),(width) (gradient colour 1)
(gradient colour 2) (scale) (-t) (-l)
Disk IO graph for reads, colours defined in hex, minus the #. If scale is non-zero, it becomes the scale for the graph. Device as in diskio. Uses a logarithmic scale (to see small numbers) when you use -l switch. Takes the switch ’-t’ to use a temperature gradient, which makes the gradient values change depending on the amplitude of a particular graph value (try it and see).
diskiograph_write (device)
(height),(width) (gradient colour 1)
(gradient colour 2) (scale) (-t) (-l)
Disk IO graph for writes, colours defined in hex, minus the #. If scale is non-zero, it becomes the scale for the graph. Device as in diskio. Uses a logarithmic scale (to see small numbers) when you use -l switch. Takes the switch ’-t’ to use a temperature gradient, which makes the gradient values change depending on the amplitude of a particular graph value (try it and see).
distribution
The name of the distribution. It could be that some of the untested distributions will show up wrong or as “unknown”, if that’s the case post a bug on sourceforge, make sure it contains the name of your distribution, the contents of and if there is a file that only exists on your distribution, also add the path of that file in the bug. If there is no such file, please add another way which we can use to identify your distribution.
downspeed (net)
Download speed in suitable IEC units.
downspeedf (net)
Download speed in KiB with one decimal.
downspeedgraph (netdev)
(height),(width) (gradient colour 1) (gradient
colour 2) (scale) (-t) (-l)
Download speed graph, colours defined in hex, minus the #. If scale is non-zero, it defines the maximum value of the graph (in bytes per second). Uses a logarithmic scale (to see small numbers) when you use -l switch. Takes the switch ’-t’ to use a temperature gradient, which makes the gradient values change depending on the amplitude of a particular graph value (try it and see).
draft_mails (maildir) (interval)
Number of mails marked as draft in the specified mailbox or mail spool if not. Only maildir type mailboxes are supported, mbox type will return -1.
|
else |
Text to show if any of the above are not true. |
|||
|
endif |
Ends an $if block. |
entropy_avail
Current entropy available for crypto freaks.
entropy_bar (height),(width)
Normalized bar of available entropy for crypto freaks.
entropy_perc
Percentage of entropy available in comparison to the poolsize.
entropy_poolsize
Total size of system entropy pool for crypto freaks.
eval string
Evaluates given string according to the rules of conky.text interpretation, i.e. parsing any contained text object specifications into their output, any occurring ’$′intoasingle′’ and so on. The output is then being parsed again.
exec command
Executes a shell command and displays the output in conky. Warning: this takes a lot more resources than other variables. I’d recommend coding wanted behaviour in C/C++ and posting a patch.
execbar (height),(width) command
Same as exec, except if the first value returned is a value between 0-100, it will use that number to draw a horizontal bar. The height and width parameters are optional, and default to the default_bar_height and default_bar_width config settings, respectively.
execgauge (height),(width) command
Same as exec, except if the first value returned is a value between 0-100, it will use that number to draw a round gauge (much like a vehicle speedometer). The height and width parameters are optional, and default to the default_gauge_height and default_gauge_width config settings, respectively.
execgraph command
(height),(width) (gradient color 1) (gradient color
2) (scale) (-t) (-l)
Draws a horizontally scrolling graph with values from 0-100 plotted on the vertical axis. All parameters following the command are optional. Gradient colors can be specified as hexadecimal values with no 0x or # prefix. Use the -t switch to enable a temperature gradient, so that small values are “cold” with color 1 and large values are “hot” with color 2. Without the -t switch, the colors produce a horizontal gradient spanning the width of the graph. The scale parameter defines the maximum value of the graph. Use the -l switch to enable a logarithmic scale, which helps to see small values. The default size for graphs can be controlled via the default_graph_height and default_graph_width config settings.
If you need to execute a command with spaces, you have a couple options:
|
1. |
wrap your command in double-quotes, or | ||
|
2. |
put your command into a separate file, such as ~/bin/myscript.sh, and use that as your execgraph command. |
Remember to make your script executable!
In the following example, we set up execgraph to display seconds (0-59) on a graph that is 50px high and 200px wide, using a temperature gradient with colors ranging from red for small values (FF0000) to yellow for large values (FFFF00). We set the scale to 60.
${execgraph ~/seconds.sh 50,200 FF0000 FFFF00 60 -t}
execi interval command
Same as exec, but with a specific interval in seconds. The interval can’t be less than the update_interval in your configuration. See also $texeci.
execibar interval (height),(width) command
Same as execbar, but with an interval.
execigauge interval (height),(width) command
Same as execgauge, but with an interval.
execigraph interval command
(height),(width) (gradient color 1)
(gradient color 2) (scale) (-t) (-l)
Same as execgraph, but with an interval.
execp command
Executes a shell command and displays the output in conky. Warning: this takes a lot more resources than other variables. I’d recommend coding wanted behaviour in C/C++ and posting a patch. This differs from $exec in that it parses the output of the command, so you can insert things like `${color red}hi!${color}` in your script and have it correctly parsed by Conky. Caveats: Conky parses and evaluates the output of $execp every time Conky loops, and then destroys all the objects. If you try to use anything like $execi within an $execp statement, it will functionally run at the same interval that the $execp statement runs, as it is created and destroyed at every interval.
execpi interval command
Same as execp, but with an interval. Note that the output from the $execpi command is still parsed and evaluated at every interval.
flagged_mails (maildir) (interval)
Number of mails marked as flagged in the specified mailbox or mail spool if not. Only maildir type mailboxes are supported, mbox type will return -1.
font (font)
Specify a different font. This new font will apply to the current line and everything following. You can use a $font with no arguments to change back to the default font (much like with $color).
|
fontN |
Change font to fontN configuration option, where N is a digit between 0 and 9, inclusively. |
format_time seconds format
Format time given in seconds. This var only works when the times_in_seconds configuration setting is on. Format is a string that should start and end with a double quote " character. The quote characters are not part of the output, ,,,(,) and \ are replaced by weeks,days,hours,minutes,seconds,(,) and . If you leave out a unit, it’s value will be expressed in the highest unit lower than the one left out. Text between ()-chars will not be visible if a replaced unit in this text is 0. If seconds is a decimal number then you can see the numbers behind the point by using followed by a number that specifies the amount of digits behind the point that you want to see (maximum 9). You can also place a ’x’ behind so you have all digits behind the point and no trailing zero’s. (also maximum 9).
forwarded_mails (maildir) (interval)
Number of mails marked as forwarded in the specified mailbox or mail spool if not. Only maildir type mailboxes are supported, mbox type will return -1.
free_bufcache
Amount of memory cached or buffered, as reported by free. Linux only.
free_cached
Amount of memory cached, as reported by free. Linux only.
freq (n)
Returns CPU #n’s frequency in MHz. CPUs are counted from 1.
Default: 1
freq2 (n)
Returns CPU #n’s clock speed from assembly in MHz. CPUs are counted from 1.
Default: 1
freq_g (n)
Returns CPU #n’s frequency in GHz. CPUs are counted from 1.
Default: 1
fs_bar (height),(width) fs
Bar that shows how much space is used on a file system. height is the height in pixels. fs is any file on that file system.
fs_bar_free (height),(width) fs
Bar that shows how much space is free on a file system. height is the height in pixels. fs is any file on that file system.
fs_free (fs)
Free space on a file system available for users.
fs_free_perc (fs)
Free percentage of space on a file system available for users.
fs_size (fs)
File system size.
fs_type (fs)
File system type.
fs_used (fs)
File system used space.
fs_used_perc (fs)
Percent of file system used space.
gid_name gid
Name of group with this gid.
github_notifications
Number of GitHub notifications.
|
goto x |
The next element will be printed at position ’x’. |
gw_iface
Displays the default route’s interface or “multiple”/“none” accordingly.
|
gw_ip |
Displays the default gateway’s IP or “multiple”/“none” accordingly. |
hddtemp (dev)
Displays temperature of a selected hard disk drive as reported by the hddtemp daemon. Use hddtemp_host and hddtemp_port to specify a host and port for all hddtemp objects. If no dev parameter is given, the first disk returned by the hddtemp daemon is used.
head logfile lines (next_check)
Displays first N lines of supplied text file. The file is checked every ’next_check’ update. If next_check is not supplied, Conky defaults to 2. Max of 30 lines can be displayed, or until the text buffer is filled.
hr (height)
Horizontal line, height is the height in pixels.
hwmon (dev) type n (factor offset)
Hwmon sensor from sysfs (Linux 2.6). Parameter dev can be: 1. Number. e.g 1 means hwmon1. 2. Module name. e.g. k10temp means the first hwmon device whose module name is `k10temp. 3. Omitted. Then the first hwmon device (hwmon0) will be used.
Parameter type is either in or vol meaning voltage; fan meaning fan; temp meaning temperature. Parameter n is number of the sensor. See /sys/class/hwmon/ on your local computer. The optional arguments factor and offset allow precalculation of the raw input, which is being modified as follows: input = input * factor + offset. Note that they have to be given as decimal values (i.e. contain at least one decimal place).
i2c (dev) type n (factor offset)
I2C sensor from sysfs (Linux 2.6). Parameter dev may be omitted if you have only one I2C device. Parameter type is either in or vol meaning voltage; fan meaning fan; temp meaning temperature. Parameter n is number of the sensor. See /sys/bus/i2c/devices/ on your local computer. The optional arguments factor and offset allow precalculation of the raw input, which is being modified as follows: input = input * factor + offset. Note that they have to be given as decimal values (i.e. contain at least one decimal place).
i8k_ac_status
If running the i8k kernel driver for Inspiron laptops, displays whether ac power is on, as listed in /proc/i8k (translated to human-readable). Beware that this is by default not enabled by i8k itself.
i8k_bios
If running the i8k kernel driver for Inspiron laptops, displays the bios version as listed in /proc/i8k.
i8k_buttons_status
If running the i8k kernel driver for Inspiron laptops, displays the volume buttons status as listed in /proc/i8k.
i8k_cpu_temp
If running the i8k kernel driver for Inspiron laptops, displays the cpu temperature in Celsius, as reported by /proc/i8k.
i8k_left_fan_rpm
If running the i8k kernel driver for Inspiron laptops, displays the left fan’s rate of rotation, in revolutions per minute as listed in /proc/i8k. Beware, some laptops i8k reports these fans in reverse order.
i8k_left_fan_status
If running the i8k kernel driver for Inspiron laptops, displays the left fan status as listed in /proc/i8k (translated to human-readable). Beware, some laptops i8k reports these fans in reverse order.
i8k_right_fan_rpm
If running the i8k kernel driver for Inspiron laptops, displays the right fan’s rate of rotation, in revolutions per minute as listed in /proc/i8k. Beware, some laptops i8k reports these fans in reverse order.
i8k_right_fan_status
If running the i8k kernel driver for Inspiron laptops, displays the right fan status as listed in /proc/i8k (translated to human-readable). Beware, some laptops i8k reports these fans in reverse order.
i8k_serial
If running the i8k kernel driver for Inspiron laptops, displays your laptop serial number as listed in /proc/i8k.
i8k_version
If running the i8k kernel driver for Inspiron laptops, displays the version formatting of /proc/i8k.
ibm_brightness
If running the IBM ACPI, displays the brigtness of the laptops’s LCD (0-7).
ibm_fan
If running the IBM ACPI, displays the fan speed.
ibm_temps N
If running the IBM ACPI, displays the temperatures from the IBM temperature sensors (N=0..7) Sensor 0 is on the CPU, 3 is on the GPU.
ibm_thinklight
If running the IBM ACPI, displays the status of your ThinkLight™. Value is either ’on’, ’off’ or ’unknown’.
ibm_volume
If running the IBM ACPI, displays the “master” volume, controlled by the volume keys (0-14).
ical number file
Shows title of event number ’number’ in the ical (RFC 5545) file ’file’. The events are first ordered by starting time, events that started in the past are ignored. The events that are shown are the VEVENTS, the title that is shown is the SUMMARY and the starting time used for sorting is DTSTART.
iconv_start codeset_from codeset_to
Convert text from one codeset to another using GNU iconv. Needs to be stopped with iconv_stop.
iconv_stop
Stop iconv codeset conversion.
if_empty (var)
if conky variable VAR is empty, display everything between $if_empty and the matching $endif.
if_existing file (string)
if FILE exists, display everything between if_existing and the matching $endif. The optional second parameter checks for FILE containing the specified string and prints everything between $if_existing and the matching $endif.
|
if_gw |
if there is at least one default gateway, display everything between $if_gw and the matching $endif. |
if_match expression
Evaluates the given boolean expression, printing everything between $if_match and the matching $endif depending on whether the evaluation returns true or not. Valid expressions consist of a left side, an operator and a right side. Left and right sides are being parsed for contained text objects before evaluation.
Recognised left and right side types are:
|
• |
double: Argument consists of only digits and a single dot. | ||
|
• |
long: Argument consists of only digits. | ||
|
• |
string: Argument is enclosed in quotation marks ("). |
Valid operands are:
|
• |
< or > |
|||
|
• |
<= or >= |
|||
|
• |
== or != |
if_mixer_mute (mixer)
If mixer exists, display everything between $if_mixer_mute and the matching $endif. If no mixer is specified, “Vol” is used.
if_mounted (mountpoint)
if MOUNTPOINT is mounted, display everything between $if_mounted and the matching $endif.
if_mpd_playing
if mpd is playing or paused, display everything between $if_mpd_playing and the matching $endif.
if_pa_sink_muted
If Pulseaudio’s default sink is muted, display everything between $if_pa_sink_muted and the corresponding $else or $endif.
if_pa_source_muted
If Pulseaudio’s default source (e.g. your microphone) is muted, display everything between $if_pa_source_muted and the corresponding $else or $endif.
if_pa_source_running
If Pulseaudio’s default source is running (e.g. a program is accessing your microphone), display everything between $if_pa_source_running and the corresponding $else or $endif.
if_running (process)
If PROCESS is running, display everything between $if_running and the corresponding $else or $endif. Note that PROCESS may be either a full command line with arguments (without the directory prefix), or simply the name of an executable. For example, either of the following will be true if there is a running process with the command line /usr/bin/conky -u 5: * ${if_running conky -u 5} or * ${if_running conky}
It is important not to include trailing spaces. For example, ${if_running conky } will be false.
if_smapi_bat_installed (INDEX)
when using smapi, if the battery with index INDEX is installed, display everything between $if_smapi_bat_installed and the matching $endif.
if_up (interface)
if INTERFACE exists and is up, display everything between $if_up and the matching $endif.
if_updatenr (updatenr)
If it’s the UPDATENR-th time that conky updates, display everything between $if_updatenr and the matching $endif. The counter resets when the highest UPDATENR is reached.
Example: {$if_updatenr 1}foo$endif{$if_updatenr 2}bar$endif{$if_updatenr 4}$endif shows foo 25% of the time followed by bar 25% of the time followed by nothing the other half of the time.
if_xmms2_connected
Display everything between $if_xmms2_connected and the matching $endif if xmms2 is running.
iface (number)
Display interface names starting from 1, eg ${iface 1}.
image (-p x,y) (-s WxH) (-n) (-f interval)
Renders an image from the path specified using Imlib2. Takes 4 optional arguments: a position, a size, a no-cache switch, and a cache flush interval. Changing the x,y position will move the position of the image, and changing the WxH will scale the image. If you specify the no-cache flag (-n), the image will not be cached. Alternately, you can specify the -f int switch to specify a cache flush interval for a particular image. Example: ${image /home/brenden/cheeseburger.jpg -p 20,20 -s 200x200} will render ’cheeseburger.jpg’ at (20,20) scaled to 200x200 pixels. Conky does not make any attempt to adjust the position (or any other formatting) of images, they are just rendered as per the arguments passed. The only reason $image is part of the conky.text section, is to allow for runtime modifications, through $execp $lua_parse, or some other method.
imap_messages (args)
Displays the number of messages in your global IMAP inbox by default. You can define individual IMAP inboxes separately by passing arguments to this object. Arguments are: “host user pass [-i interval (in seconds)] [-f ’folder’] [-p port] [-e ’command’] [-r retries]”. Default port is 143, default folder is ’INBOX’, default interval is 5 minutes, and default number of retries before giving up is 5. If the password is supplied as ’*’, you will be prompted to enter the password when Conky starts.
imap_unseen (args)
Displays the number of unseen messages in your global IMAP inbox by default. You can define individual IMAP inboxes separately by passing arguments to this object. Arguments are: “host user pass [-i interval (in seconds)] [-f ’folder’] [-p port] [-e ’command’] [-r retries]”. Default port is 143, default folder is ’INBOX’, default interval is 5 minutes, and default number of retries before giving up is 5. If the password is supplied as ’*’, you will be prompted to enter the password when Conky starts.
intel_backlight
Display the brightness of your Intel backlight in percent.
ioscheduler disk
Prints the current ioscheduler used for the given disk name (i.e. e.g. “hda” or “sdb”).
irc server(:port) #channel (max_msg_lines)
Shows everything that’s being told in #channel on IRCserver ’server’. TCP-port 6667 is used for the connection unless ’port’ is specified. Shows everything since the last time or the last ’max_msg_lines’ entries if specified.
journal lines (type)
Displays last N lines of the systemd journal. The optional type can be ’user’ or ’system’ which will show only the user or system journal respectively. By default, all journal lines visible to the user are shown. A maximum of 200 lines can be displayed, or until the text buffer is filled.
|
kernel |
Kernel version. |
key_caps_lock
An indicator for Capital Lock key.
key_num_lock
An indicator for Number Lock key.
key_scroll_lock
An indicator for Scrolling Lock key.
keyboard_layout
Display keyboard layout.
laptop_mode
The value of /proc/sys/vm/laptop_mode.
legacymem
Amount of memory used, calculated the same way as in the free program.
lines textfile
Displays the number of lines in the given file.
loadavg (1|2|3)
System load average, 1 is for past 1 minute, 2 for past 5 minutes and 3 for past 15 minutes. Without argument, prints all three values separated by whitespace.
loadgraph (height),(width)
(gradient colour 1) (gradient colour 2)
(scale) (-t) (-l)
Load1 average graph, similar to xload, with optional colours in hex, minus the #. Uses a logarithmic scale (to see small numbers) when you use the -l switch. Takes the switch ’-t’ to use a temperature gradient, which makes the gradient values change depending on the amplitude of a particular graph value (try it and see).
lowercase text
Converts all letters into lowercase.
lua function_name (function parameters)
Executes a Lua function with given parameters, then prints the returned string. See also ’lua_load’ on how to load scripts. Conky puts ’conky_’ in front of function_name to prevent accidental calls to the wrong function unless you place ’conky_’ in front of it yourself.
lua_bar (height,width) function_name (function parameters)
Executes a Lua function with given parameters and draws a bar. Expects result value to be an integer between 0 and 100. See also ’lua_load’ on how to load scripts. Conky puts ’conky_’ in front of function_name to prevent accidental calls to the wrong function unless you place ’conky_’ in front of it yourself.
lua_gauge (height,width) function_name (function parameters)
Executes a Lua function with given parameters and draws a gauge. Expects result value to be an integer between 0 and 100. See also ’lua_load’ on how to load scripts. Conky puts ’conky_’ in front of function_name to prevent accidental calls to the wrong function unless you place ’conky_’ in front of it yourself.
lua_graph function_name
(height),(width) (gradient colour 1) (gradient
colour 2) (scale) (-t) (-l)
Executes a Lua function with and draws a graph. Expects result value to be any number, and by default will scale to show the full range. See also ’lua_load’ on how to load scripts. Takes the switch ’-t’ to use a temperature gradient, which makes the gradient values change depending on the amplitude of a particular graph value (try it and see). Conky puts ’conky_’ in front of function_name to prevent accidental calls to the wrong function unless you put you place ’conky_’ in front of it yourself.
lua_parse function_name (function parameters)
Executes a Lua function with given parameters as per $lua, then parses and prints the result value as per the syntax for the conky.text section. See also ’lua_load’ on how to load scripts. Conky puts ’conky_’ in front of function_name to prevent accidental calls to the wrong function unless you place ’conky_’ in front of it yourself.
machine
Machine, e.g. i686, x86_64.
mails (mailbox) (interval)
Mail count in the specified mailbox or your mail spool if not. Both mbox and maildir type mailboxes are supported. You can use a program like fetchmail to get mails from some server using your favourite protocol. See also new_mails.
mboxscan (-n number of
messages to print) (-fw from width) (-sw subject
width) mbox
Print a summary of recent messages in an mbox format mailbox. mbox parameter is the filename of the mailbox (can be encapsulated using ’“’, ie. ${mboxscan -n 10”/home/brenden/some box”}
|
mem |
Amount of memory in use. |
memactive
Amount of active memory. FreeBSD only.
memavail
Amount of available memory as recorded in /proc/meminfo. Linux 3.14+ only.
membar (height),(width)
Bar that shows amount of memory in use.
memdirty
Amount of “dirty” memory. Linux only.
memeasyfree
Amount of free memory including the memory that is very easily freed (buffers/cache).
memfree
Amount of free memory.
memgauge (height),(width)
Gauge that shows amount of memory in use (see cpugauge).
memgraph (height),(width)
(gradient colour 1) (gradient colour 2)
(scale) (-t) (-l)
Memory usage graph. Uses a logarithmic scale (to see small numbers) when you use the -l switch. Takes the switch ’-t’ to use a temperature gradient, which makes the gradient values change depending on the amplitude of a particular graph value (try it and see).
meminactive
Amount of inactive memory. FreeBSD only.
memlaundry
Amount of memory in the laundry queue. FreeBSD only.
|
memmax |
Total amount of memory. |
memperc
Percentage of memory in use.
memwired
Amount of wired memory. FreeBSD only.
memwithbuffers
Amount of memory in use, including that used by system buffers and caches.
memwithbuffersbar (height),(width)
Bar that shows amount of memory in use (including memory used by system buffers and caches).
memwithbuffersgraph
(height),(width) (gradient colour 1) (gradient
colour 2) (scale) (-t) (-l)
Memory usage graph including memory used by system buffers and cache. Uses a logarithmic scale (to see small numbers) when you use the -l switch. Takes the switch ’-t’ to use a temperature gradient, which makes the gradient values change depending on the amplitude of a particular graph value (try it and see).
mixer (device)
Prints the mixer value as reported by the OS. On Linux, this variable uses the OSS emulation, so you need the proper kernel module loaded. Default mixer is “Vol”, but you can specify one of the available OSS controls: “Vol”, “Bass”, “Trebl”, “Synth”, “Pcm”, “Spkr”, “Line”, “Mic”, “CD”, “Mix”, “Pcm2”, “Rec”, “IGain”, “OGain”, “Line1”, “Line2”, “Line3”, “Digital1”, “Digital2”, “Digital3”, “PhoneIn”, “PhoneOut”, “Video”, “Radio” and “Monitor”.
Default: Vol
mixerbar (device)
Displays mixer value in a bar as reported by the OS. See docs for $mixer for details on arguments.
mixerl (device)
Prints the left channel mixer value as reported by the OS. See docs for $mixer for details on arguments.
mixerlbar (device)
Displays the left channel mixer value in a bar as reported by the OS. See docs for $mixer for details on arguments.
mixerr (device)
Prints the right channel mixer value as reported by the OS. See docs for $mixer for details on arguments.
mixerrbar (device)
Displays the right channel mixer value in a bar as reported by the OS. See docs for $mixer for details on arguments.
moc_album
Album of the current MOC song.
moc_artist
Artist of the current MOC song.
moc_bitrate
Bitrate in the current MOC song.
moc_curtime
Current time of the current MOC song.
moc_file
File name of the current MOC song.
moc_rate
Rate of the current MOC song.
moc_song
The current song name being played in MOC.
moc_state
Current state of MOC; playing, stopped etc.
moc_timeleft
Time left in the current MOC song.
moc_title
Title of the current MOC song.
moc_totaltime
Total length of the current MOC song.
monitor
Number of the monitor on which conky is running or the message “Not running in X” if this is the case.
monitor_number
Number of monitors or the message “Not running in X” if this is the case.
mouse_speed
Display mouse speed.
mpd_album
Album in current MPD song.
mpd_albumartist
Artist of the album of the current MPD song.
mpd_artist
Artist in current MPD song must be enabled at compile.
mpd_bar (height),(width)
Bar of mpd’s progress.
mpd_bitrate
Bitrate of current song.
mpd_comment (max length)
Comment of current MPD song.
mpd_date
Date of current song.
mpd_elapsed
Song’s elapsed time.
mpd_file
Prints the file name of the current MPD song.
mpd_length
Song’s length.
mpd_name
Prints the MPD name field.
mpd_percent
Percent of song’s progress.
mpd_random
Random status (On/Off).
mpd_repeat
Repeat status (On/Off).
mpd_smart (max length)
Prints the song name in either the form “artist - title” or file name, depending on whats available.
mpd_status
Playing, stopped, et cetera.
mpd_title (max length)
Title of current MPD song.
mpd_track
Prints the MPD track field.
mpd_vol
MPD’s volume.
mysql query
Shows the first field of the first row of the result of the query.
nameserver (index)
Print a nameserver from /etc/resolv.conf.
new_mails (mailbox) (interval)
Unread mail count in the specified mailbox or mail spool if not. Both mbox and maildir type mailboxes are supported.
no_update text
Shows text and parses the vars in it, but doesn’t update them. Use this for things that do not change while conky is running, like $machine, $conky_version,... By not updating this you can save some resources.
nodename
Hostname.
nodename_short
Short hostname (same as ’hostname -s’ shell command).
nvidia argument (GPU_ID)
Nvidia graphics card information via the XNVCtrl library.
Temperatures are printed as float, all other values as integers.
GPU_ID: Optional parameter to choose the GPU to be used as 0,1,2,3,.. Default parameter is 0
Possible arguments:

nvidiabar (height),(width) argument (GPU_ID)
Same as nvidia, except it draws its output in a horizontal bar. The height and width parameters are optional, and default to the default_bar_height and default_bar_width config settings, respectively.
GPU_ID: Optional parameter to choose the GPU to be used as 0,1,2,3,.. Default parameter is 0
Note the following arguments are incompatible:
|
• |
gputempthreshold (threshold) |
|||
|
• |
gpufreqmin |
|||
|
• |
gpufreqmax |
|||
|
• |
memfreqmin |
|||
|
• |
memfreqmax |
|||
|
• |
mtrfreqmin |
|||
|
• |
mtrfreqmax |
|||
|
• |
perflevelmin |
|||
|
• |
perflevelmax |
|||
|
• |
perfmode |
|||
|
• |
memtotal (memmax) |
|||
|
• |
fanspeed |
nvidiagauge (height),(width) argument (GPU_ID)
Same as nvidiabar, except a round gauge (much like a vehicle speedometer). The height and width parameters are optional, and default to the default_gauge_height and default_gauge_width config settings, respectively.
GPU_ID: Optional parameter to choose the GPU to be used as 0,1,2,3,.. Default parameter is 0
For possible arguments see nvidia and nvidiabar.
nvidiagraph argument
(height),(width) (gradient color 1) (gradient
color 2) (scale) (-t) (-l) GPU_ID
Same as nvidiabar, except a horizontally scrolling graph with values from 0-100 plotted on the vertical axis. The height and width parameters are optional, and default to the default_graph_height and default_graph_width config settings, respectively.
GPU_ID: NOT optional. This parameter allows to choose the GPU to be used as 0,1,2,3,..
For possible arguments see nvidia and nvidiabar. To learn more about the -t -l and gradient color options, see execgraph.
offset (pixels)
Move text over by N pixels. See also $voffset.
outlinecolor (color)
Change outline color.
pa_card_active_profile
Pulseaudio’s default card active profile.
pa_card_name
Pulseaudio’s default card name.
pa_sink_active_port_description
Pulseaudio’s default sink active port description.
pa_sink_active_port_name
Pulseaudio’s default sink active port name.
pa_sink_description
Pulseaudio’s default sink description.
pa_sink_volume
Pulseaudio’s default sink volume percentage.
pa_sink_volumebar
Pulseaudio’s default sink volume bar.
password (length)
Generate random passwords.
pb_battery item
If running on Apple powerbook/ibook, display information on battery status. The item parameter specifies, what information to display. Exactly one item must be specified. Valid items are:

pid_chroot pid
Directory used as rootdirectory by the process (this will be “/” unless the process did a chroot syscall).
pid_cmdline pid
Command line this process was invoked with.
pid_cwd pid
Current working directory of the process.
pid_egid pid
The effective gid of the process.
pid_environ pid varname
Contents of a environment-var of the process.
pid_environ_list pid
List of environment-vars that the process can see.
pid_euid pid
The effective uid of the process.
pid_exe pid
Path to executed command that started the process.
pid_fsgid pid
The file system gid of the process.
pid_fsuid pid
The file system uid of the process.
pid_gid pid
The real gid of the process.
pid_nice pid
The nice value of the process.
pid_openfiles pid
List of files that the process has open.
pid_parent pid
The pid of the parent of the process.
pid_priority pid
The priority of the process (see ’priority’ in “man 5 proc”).
pid_read pid
Total number of bytes read by the process.
pid_sgid pid
The saved set gid of the process.
pid_state pid
State of the process.
pid_state_short pid
One of the chars in “RSDZTW” representing the state of the process where R is running, S is sleeping in an interruptible wait, D is waiting in uninterruptible disk sleep, Z is zombie, T is traced or stopped (on a signal), and W is paging.
pid_stderr pid
Filedescriptor binded to the STDERR of the process.
pid_stdin pid
Filedescriptor binded to the STDIN of the process.
pid_stdout pid
Filedescriptor binded to the STDOUT of the process.
pid_suid pid
The saved set uid of the process.
pid_thread_list pid
List with pid’s from threads from this process.
pid_threads pid
Number of threads in process containing this thread.
pid_time pid
Sum of $pid_time_kernelmode and $pid_time_usermode.
pid_time_kernelmode pid
Amount of time that the process has been scheduled in kernel mode in seconds.
pid_time_usermode pid
Amount of time that the process has been scheduled in user mode in seconds.
pid_uid pid
The real uid of the process.
pid_vmdata pid
Data segment size of the process.
pid_vmexe pid
Text segment size of the process.
pid_vmhwm pid
Peak resident set size (“high water mark”) of the process.
pid_vmlck pid
Locked memory size of the process.
pid_vmlib pid
Shared library code size of the process.
pid_vmpeak pid
Peak virtual memory size of the process.
pid_vmpte pid
Page table entries size of the process.
pid_vmrss pid
Resident set size of the process.
pid_vmsize pid
Virtual memory size of the process.
pid_vmstk pid
Stack segment size of the process.
pid_write pid
Total number of bytes written by the process.
platform (dev) type n (factor offset)
Platform sensor from sysfs (Linux 2.6). Parameter dev may be omitted if you have only one platform device. Platform type is either in or vol meaning voltage; fan meaning fan; temp meaning temperature. Parameter n is number of the sensor. See /sys/bus/platform/devices/ on your local computer. The optional arguments factor and offset allow precalculation of the raw input, which is being modified as follows: input = input * factor + offset. Note that they have to be given as decimal values (i.e. contain at least one decimal place).
pop3_unseen (args)
Displays the number of unseen messages in your global POP3 inbox by default. You can define individual POP3 inboxes separately by passing arguments to this object. Arguments are: “host user pass [-i interval (in seconds)] [-p port] [-e ’command’] [-r retries]”. Default port is 110, default interval is 5 minutes, and default number of retries before giving up is 5. If the password is supplied as ’*’, you will be prompted to enter the password when Conky starts.
pop3_used (args)
Displays the amount of space (in MiB, 2^20) used in your global POP3 inbox by default. You can define individual POP3 inboxes separately by passing arguments to this object. Arguments are: “host user pass [-i interval (in seconds)] [-p port] [-e ’command’] [-r retries]”. Default port is 110, default interval is 5 minutes, and default number of retries before giving up is 5. If the password is supplied as ’*’, you will be prompted to enter the password when Conky starts.
processes
Total processes (sleeping and running).
read_tcp (host) port
Connects to a tcp port on a host (default is localhost), reads every char available at the moment and shows them.
read_udp (host) port
Connects to a udp port on a host (default is localhost), reads every char available at the moment and shows them.
replied_mails (maildir) (interval)
Number of mails marked as replied in the specified mailbox or mail spool if not. Only maildir type mailboxes are supported, mbox type will return -1.
rss uri interval_in_seconds action (num_par (spaces_in_front))
Download and parse RSS feeds. The interval may be a (floating point) value greater than 0. Action may be one of the following: feed_title, item_title (with num par), item_desc (with num par) and item_titles (when using this action and spaces_in_front is given conky places that many spaces in front of each item). This object is threaded, and once a thread is created it can’t be explicitly destroyed. One thread will run for each URI specified. You can use any protocol that Curl supports.
rstrip text
Strips all trailing whitespace from input.
running_processes
Running processes (not sleeping). Requires Linux 2.6.
running_threads
Number of running (runnable) threads. Linux only.
scroll (direction) length (step) (interval) text
Scroll ’text’ by ’step’ characters to the left or right (set ’direction’ to ’left’ or ’right’ or ’wait’) showing ’length’ number of characters at the same time. The text may also contain variables. ’step’ is optional and defaults to 1 if not set. ’direction’ is optional and defaults to left if not set. When direction is ’wait’ then text will scroll left and wait for ’interval’ itertations at the beginning and end of the text. If a var creates output on multiple lines then the lines are placed behind each other separated with a ’|’-sign. If you change the textcolor inside $scroll it will automatically have it’s old value back at the end of $scroll. The end and the start of text will be separated by ’length’ number of spaces unless direction is ’wait’.
seen_mails (maildir) (interval)
Number of mails marked as seen in the specified mailbox or mail spool if not. Only maildir type mailboxes are supported, mbox type will return -1.
shadecolor (color)
Change shading color.
|
shmem |
Amount of shared memory. Linux only. |
sip_status (switch)
Prints info regarding System Integrity Protection (SIP) on macOS. If no switch is provided, prints SIP status (enabled / disabled), else, status of the specific SIP feature corresponding to the switch provided.
Below are shown the available switches:
uses unsupported configuration?: If yes, prints “unsupported configuration, beware!” Else, prints “configuration is ok”.
USAGE:
$ conky -t '${sip_status}'
# print SIP status
$ conky -t '${sip_status 0}'
# print allows apple-internal? Yes or No?
NOTES:
|
• |
Available for all macOS versions (even the ones prior El Capitan where SIP was first introduced) | ||
|
• |
If run on versions prior El Capitan SIP is unavailable, so all you will get is “unsupported”. |
smapi (ARGS)
When using smapi, display contents of the /sys/devices/platform/smapi directory. ARGS are either (FILENAME) or bat (INDEX) (FILENAME) to display the corresponding files’ content. This is a very raw method of accessing the smapi values. When available, better use one of the smapi_* variables instead.
smapi_bat_bar (INDEX),(height),(width)
when using smapi, display the remaining capacity of the battery with index INDEX as a bar.
smapi_bat_perc (INDEX)
when using smapi, display the remaining capacity in percent of the battery with index INDEX. This is a separate variable because it supports the ’use_spacer’ configuration option.
smapi_bat_power INDEX
when using smapi, display the current power of the battery with index INDEX in watt. This is a separate variable because the original read out value is being converted from mW. The sign of the output reflects charging (positive) or discharging (negative) state.
smapi_bat_temp INDEX
when using smapi, display the current temperature of the battery with index INDEX in degree Celsius. This is a separate variable because the original read out value is being converted from milli degree Celsius.
sony_fanspeed
Displays the Sony VAIO fanspeed information if sony-laptop kernel support is enabled. Linux only.
startcase text
Capitalises the start of each word.
stippled_hr (space)
Stippled (dashed) horizontal line.
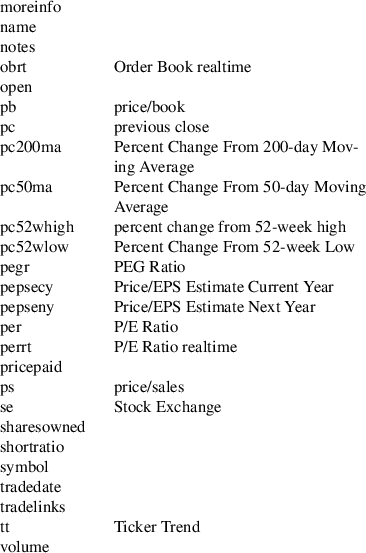
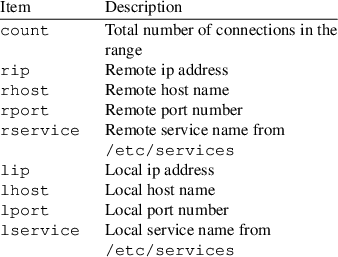
stock symbol data
Displays the data of a stock symbol. The following data is supported:
|
swap |
Amount of swap in use. |
swapbar (height),(width)
Bar that shows amount of swap in use.
swapfree
Amount of free swap.
swapmax
Total amount of swap.
swapperc
Percentage of swap in use.
sysctlbyname (name)
Print sysctl value by name. FreeBSD only.
sysname
System name, e.g. Linux.
tab (width, (start))
Puts a tab of the specified width, starting from column ’start’. The unit is pixels for both arguments.
tail logfile lines (next_check)
Displays last N lines of supplied text file. The file is checked every ’next_check’ update. If next_check is not supplied, Conky defaults to 2. Max of 30 lines can be displayed, or until the text buffer is filled.
tcp_ping host (port)
Displays the number of microseconds it takes to get a reply on a ping to to tcp ’port’ on ’host’. ’port’ is optional and has 80 as default. This works on both open and closed ports, just make sure that the port is not behind a firewall or you will get ’down’ as answer. It’s best to test a closed port instead of an open port, you will get a quicker response.
tcp_portmon port_begin port_end item (index)
TCP port (both IPv6 and IPv4) monitor for specified local ports. Port numbers must be in the range 1 to 65535. Valid items are:
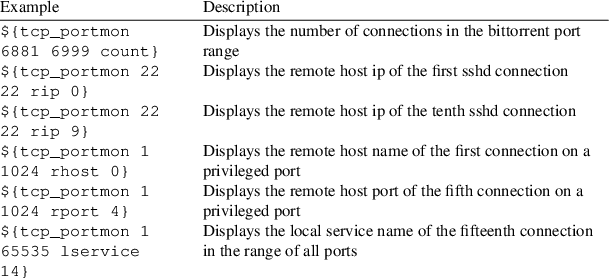
The connection index provides you with access to each connection in the port monitor. The monitor will return information for index values from 0 to n-1 connections. Values higher than n-1 are simply ignored. For the count item, the connection index must be omitted. It is required for all other items.
Examples:

Note that port monitor variables which share the same port range actually refer to the same monitor, so many references to a single port range for different items and different indexes all use the same monitor internally. In other words, the program avoids creating redundant monitors.
templateN (arg1) (arg2) (arg3 ...)
Evaluate the content of the templateN configuration variable (where N is a value between 0 and 9, inclusively), applying substitutions as described in the documentation of the corresponding configuration variable. The number of arguments is optional, but must match the highest referred index in the template. You can use the same special sequences in each argument as the ones valid for a template definition, e.g. to allow an argument to contain a whitespace. Also simple nesting of templates is possible this way.
Here are some examples of template definitions, note they are placed between [[ ... ]] instead of ...:
template0 = [[$12]]
template1 = [[1: ${fs_used 2} / ${fs_size 2}]]
template2 = [[1 2]]
The following list shows sample usage of the templates defined above, with the equivalent syntax when not using any template at all:

texeci interval command
Runs a command at an interval inside a thread and displays the output. Same as $execi, except the command is run inside a thread. Use this if you have a slow script to keep Conky updating. You should make the interval slightly longer than the time it takes your script to execute. For example, if you have a script that take 5 seconds to execute, you should make the interval at least 6 seconds. See also $execi. This object will clean up the thread when it is destroyed, so it can safely be used in a nested fashion, though it may not produce the desired behaviour if used this way.
texecpi interval command
Same as execpi, except the command is run inside a thread.
threads
Total threads.
time (format)
Local time, see “man strftime” to get more information about format.
to_bytes size
If ’size’ is a number followed by a size-unit (kilobyte,mb,GiB,...) then it converts the size to bytes and shows it without unit, otherwise it just shows ’size’.
top type num
This takes arguments in the form:top (name) (number) Basically, processes are ranked from highest to lowest in terms of cpu usage, which is what (num) represents. The types are: “name”, “pid”, “cpu”, “mem”, “mem_res”, “mem_vsize”, “time”, “uid”, “user”, “io_perc”, “io_read” and “io_write”. There can be a max of 10 processes listed.
top_io type num
Same as top, except sorted by the amount of I/O the process has done during the update interval.
top_mem type num
Same as top, except sorted by mem usage instead of cpu.
top_time type num
Same as top, except sorted by total CPU time instead of current CPU usage.
totaldown (net)
Total download, overflows at 4 GB on Linux with 32-bit arch and there doesn’t seem to be a way to know how many times it has already done that before conky has started.
totalup (net)
Total upload, this one too, may overflow.
trashed_mails (maildir) (interval)
Number of mails marked as trashed in the specified mailbox or mail spool if not. Only maildir type mailboxes are supported, mbox type will return -1.
tztime (timezone (format))
Local time for specified timezone, see man strftime to get more information about format. The timezone argument is specified in similar fashion as TZ environment variable. For hints, look in /usr/share/zoneinfo. e.g. US/Pacific, Europe/Zurich, etc.
uid_name uid
Username of user with this uid.
unflagged_mails (maildir) (interval)
Number of mails not marked as flagged in the specified mailbox or mail spool if not. Only maildir type mailboxes are supported, mbox type will return -1.
unforwarded_mails (maildir) (interval)
Number of mails not marked as forwarded in the specified mailbox or mail spool if not. Only maildir type mailboxes are supported, mbox type will return -1.
unreplied_mails (maildir) (interval)
Number of mails not marked as replied in the specified mailbox or mail spool if not. Only maildir type mailboxes are supported, mbox type will return -1.
unseen_mails (maildir) (interval)
Number of new or unseen mails in the specified mailbox or mail spool if not. Only maildir type mailboxes are supported, mbox type will return -1.
updates Number of updates
for debugging.
uppercase text
Converts all letters into uppercase.
upspeed (net)
Upload speed in suitable IEC units.
upspeedf (net)
Upload speed in KiB with one decimal.
upspeedgraph (netdev)
(height),(width) (gradient colour 1) (gradient
colour 2) (scale) (-t) (-l)
Upload speed graph, colours defined in hex, minus the #. If scale is non-zero, it defines the maximum value of the graph (in bytes per second). Uses a logarithmic scale (to see small numbers) when you use the -l switch. Takes the switch ’-t’ to use a temperature gradient, which makes the gradient values change depending on the amplitude of a particular graph value (try it and see).
|
uptime |
Uptime. |
uptime_short
Uptime in a shorter format.
user_names
Lists the names of the users logged in.
user_number
Number of users logged in.
user_terms
Lists the consoles in use.
user_time console
Lists how long the user for the given console has been logged in for.
user_times
Lists how long users have been logged in for.
utime (format)
Display time in UTC (universal coordinate time).
v6addrs (-n) (-s) (interface)
IPv6 addresses for an interface, followed by netmask if -n is specified and scope with -s. Scopes are Global(G), Host-local(H), Link-local(L), Site-local(S), Compat(C) and Unspecified(/). Linux only.
version
Git version number. DragonFly only.
voffset (pixels)
Change vertical offset by N pixels. Negative values will cause text to overlap. See also $offset.
voltage_mv (n)
Returns CPU #n’s voltage in mV. CPUs are counted from 1.
Default: 1
voltage_v (n)
Returns CPU #n’s voltage in V. CPUs are counted from 1.
Default: 1
wireless_ap (net)
Wireless access point MAC address. Linux only.
wireless_bitrate (net)
Wireless bitrate (ie 11 Mb/s). Linux only.
wireless_channel (net)
WLAN channel on which device ’net’ is listening.
wireless_essid (net)
Wireless access point ESSID. Linux only.
wireless_freq (net)
Frequency on which device ’net’ is listening.
wireless_link_bar (height),(width) (net)
Wireless link quality bar. Linux only.
wireless_link_qual (net)
Wireless link quality. Linux only.
wireless_link_qual_max (net)
Wireless link quality maximum value. Linux only.
wireless_link_qual_perc (net)
Wireless link quality in percents. Linux only.
wireless_mode (net)
Wireless mode (Managed/Ad-Hoc/Master). Linux only.
words textfile
Displays the number of words in the given file.
xmms2_album
Album in current XMMS2 song.
xmms2_artist
Artist in current XMMS2 song.
xmms2_bar (height),(width)
Bar of XMMS2’s progress.
xmms2_bitrate
Bitrate of current song.
xmms2_comment
Comment in current XMMS2 song.
xmms2_date
Returns song’s date.
xmms2_duration
Duration of current song.
xmms2_elapsed
Song’s elapsed time.
xmms2_genre
Genre in current XMMS2 song.
xmms2_id
XMMS2 id of current song.
xmms2_percent
Percent of song’s progress.
xmms2_playlist
Returns the XMMS2 playlist.
xmms2_size
Size of current song.
xmms2_smart
Prints the song name in either the form “artist - title” or file name, depending on whats available.
xmms2_status
XMMS2 status (Playing, Paused, Stopped, or Disconnected).
xmms2_timesplayed
Number of times a song was played (presumably).
xmms2_title
Title in current XMMS2 song.
xmms2_tracknr
Track number in current XMMS2 song.
xmms2_url
Full path to current song.
LUA API
Conky features a Lua Programming API, and also ships with Lua bindings for some useful libraries. Note that the bindings require tolua++, which currently only compiles against Lua 5.1.
To use Lua Conky, you first need to make sure you have a version of Conky with Lua support enabled (conky -v will report this). Conky defines certain global functions and variables which can be accessed from Lua code running in Conky. Scripts must first be loaded using the lua_load configuration option. You then call functions in Lua via Conky’s $lua, $lua_read, and Lua hooks.
Be careful when creating threaded objects through the Lua API. You could wind up with a whole bunch of threads running if a thread is created with each iteration.
NOTE: In order
to accommodate certain features in the cairo library’s
API, Conky will export a few additional functions for the
creation of certain structures. These are documented below.
RsvgDimensionData:create()
Call this method to return a new RsvgDimensionData structure. A creation function for this structure is not provided by the Rsvg API.
After calling this, you should use tolua.takeownership(rect) on the return value to ensure ownership is passed properly.
RsvgDimensionData:destroy()
Call this method to free memory allocated by RsvgDimensionData:create.
You should call tolua.releaseownership(dd) before calling this function to avoid double-frees, but only if you previously called tolua.takeownership(dd)
RsvgDimensionData:get()
Gets the values of an existing RsvgDimensionData.
RsvgDimensionData:set(x, y, width, height)
Sets the values of an existing RsvgDimensionData.
RsvgRectangle:create()
Call this method to return a new RsvgRectangle structure. A creation function for this structure is not provided by the Rsvg API.
After calling this, you should use tolua.takeownership(rect) on the return value to ensure ownership is passed properly.
RsvgRectangle:destroy()
Call this method to free memory allocated by RsvgRectangle:create.
You should call tolua.releaseownership(rect) before calling this function to avoid double-frees, but only if you previously called tolua.takeownership(rect)
RsvgRectangle:get()
Gets the values of an existing RsvgRectangle.
RsvgRectangle:set(x, y, width, height)
Sets the values of an existing RsvgRectangle.
cairo_font_extents_t:create()
Call this function to return a new cairo_font_extents_t structure. A creation function for this structure is not provided by the cairo API.
After calling this, you should use tolua.takeownership(cfe) on the return value to ensure ownership is passed properly.
cairo_font_extents_t:destroy(structure)
Call this function to free memory allocated by cairo_font_extents_t:create.
You should call tolua.releaseownership(cfe) before calling this function to avoid double-frees, but only if you previously called tolua.takeownership(cfe)
cairo_matrix_t:create()
Call this function to return a new cairo_matrix_t structure. A creation function for this structure is not provided by the cairo API.
After calling this, you should use tolua.takeownership(cm) on the return value to ensure ownership is passed properly.
cairo_matrix_t:destroy(structure)
Call this function to free memory allocated by cairo_matrix_t:create.
You should call tolua.releaseownership(cm) before calling this function to avoid double-frees, but only if you previously called tolua.takeownership(cm)
cairo_place_image(file, cr, x, y, width, height, alpha)
Renders an image onto a cairo_t, using imlib2. In some cases using a cairo_t and exact coordinates is more useful.
require(’cairo_imlib2_helper’) in your lua file.
cairo_text_extents_t:create()
Call this function to return a new cairo_text_extents_t structure. A creation function for this structure is not provided by the cairo API.
After calling this, you should use tolua.takeownership(cte) on the return value to ensure ownership is passed properly.
cairo_text_extents_t:destroy(structure)
Call this function to free memory allocated by cairo_text_extents_t:create.
You should call tolua.releaseownership(cte) before calling this function to avoid double-frees, but only if you previously called tolua.takeownership(cte)
conky_build_arch
A string containing the build architecture for this particular instance of Conky.
conky_build_info
A string containing the build info for this particular instance of Conky, including the version, build date, and architecture.
conky_config
A string containing the path of the current Conky configuration file.
conky_info
This table contains some information about Conky’s internal data. The following table describes the values contained:

conky_parse(string)
This function takes a string that is evaluated as per Conky’s TEXT section, and then returns a string with the result.
conky_set_update_interval(number)
Sets Conky’s update interval (in seconds) to ’number’.
conky_version
A string containing the version of the current instance of Conky.
conky_window
This table contains some information about Conky’s window. The following table describes the values contained:

NOTE: This table is only defined when X support is enabled.
ret_scale_x,ret_scale_y:cairo_draw_image(file,
cs, x, y, scale_x,
scale_y)
Renders an image onto a cairo_surface_t, using imlib2. Returns the amount the image was scaled by

require(’cairo_imlib2_helper’) in your lua file.
EXAMPLES
conky -t '${time %D %H:%M}' -o -u 30
Start Conky in its own window with date and clock as text and 30 sec update interval.
conky -a top_left -x 5 -y 500 -d
Start Conky to background at coordinates (5, 500).
conky -C > ~/.config/conky/conky.conf
Do not start Conky, but have it output the builtin default config file to ~/.config/conky/conky.conf for later customising.
FILES
${sysconfdir}/conky/conky.conf
Default system-wide configuration file. The value of ${sysconfdir} depends on the compile-time options (most likely /etc).
~/.config/conky/conky.conf
Default personal configuration file.
BUGS
Drawing to root or some other desktop window directly doesn't work with all window managers. Especially doesn't work well with Gnome and it has been reported that it doesn't work with KDE either. Nautilus can be disabled from drawing to desktop with program gconf-editor. Uncheck show_desktop in /apps/nautilus/preferences/. There is -w switch in Conky to set some specific window id. You might find xwininfo -tree useful to find the window to draw to. You can also use -o argument which makes Conky to create its own window. If you do try running Conky in its own window, be sure to read up on the own_window_type settings and experiment.
SEE ALSO
https://github.com/brndnmtthws/conky
COPYING
Copyright (c) 2005-2024 Brenden Matthews, Philip Kovacs, et. al. Any original torsmo code is licensed under the BSD license (see LICENSE.BSD for a copy). All code written since the fork of torsmo is licensed under the GPL (see LICENSE.GPL for a copy), except where noted differently (such as in portmon and audacious code which are LGPL, and prss which is an MIT-style license).
AUTHORS
The Conky dev team (see AUTHORS for a full list of contributors).